Science
Have you ever wondered how we perceive different colours? It all begins with light! Light is a type of energy that travels in waves, and each colour has different wavelengths. When light strikes something, some of these wavelengths are absorbed, while others bounce off. The colours we see are the wavelengths that bounce off.
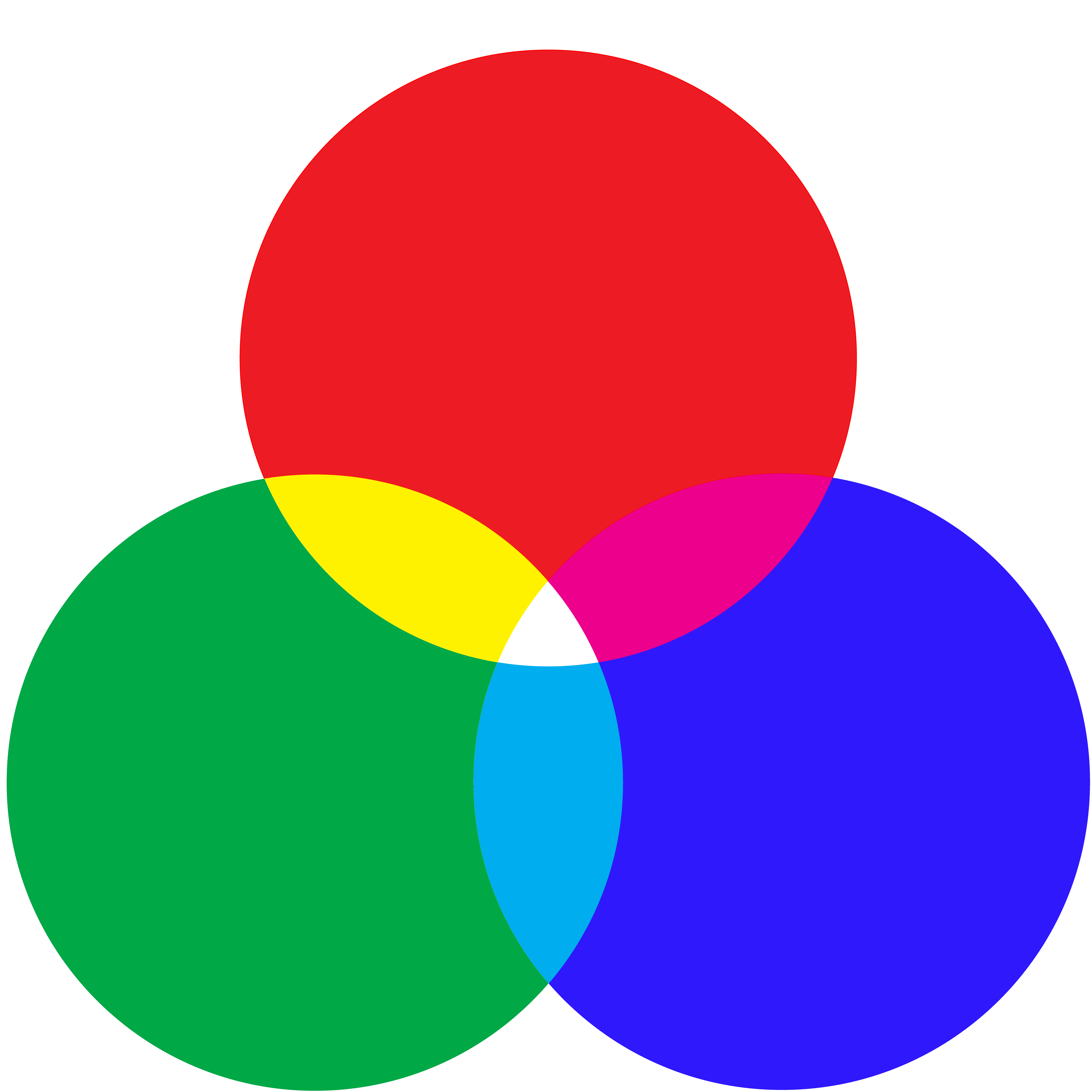
Our eyes are designed to detect these reflected colours. Inside the eye, there's a part called the retina, which is like a tiny movie screen. The retina has two types of tiny cells – rods and cones. Rods help us see in low light, while cones are experts at perceiving colour. We have three types of cones, each sensitive to different colours: red, green, and blue.
When light enters our eyes, the cones react to the different wavelengths. They send signals to the brain saying, "Hey, we've found red!" or "I'm seeing a lot of green!" The brain then mixes these signals together to create all the colours we see.
The brain mixes the primary colours (red, green, and blue) to create every possible shade. For example, when the red and green cones send equally strong signals, the brain says, "This must be yellow!" This process of mixing colours is constantly happening as we look around, giving us a colourful world.
Sometimes, people are born with colour vision that works differently. The most common type of colour blindness occurs when the red and green cones are more similar than usual, making it hard to distinguish between these colours. This is why some people might mix up red and green. There are other types of colour blindness, but they're less common.
Seeing colour is a joint effort between our eyes and brain. Light reflects off objects, our eyes detect the different wavelengths, and our brain mixes them together to create the world we see. It's a fascinating process that occurs in a split second, allowing us to appreciate the beauty of a colourful sunset, a vibrant painting, or a field of flowers. So the next time you spot a rainbow, remember the incredible science behind it!